802.11n WiFi Standard Finally Approved!
 Saturday, September 12, 2009 at 10:15AM
Saturday, September 12, 2009 at 10:15AM Has it been really 7 years!? There were early leaks posted on various sites the IEEE was close to an approval. Sites are reporting a formal announcement from the IEEE next week. 802.11n will bring 160+ mbps actual throughput to wireless users. This is 7x’s faster than the current 802.11a/g technology. I expect to see more enterprise customers taking full advantage of 802.11n in future deployments with this final approval.
Specific to Cisco 802.11n – Things to note:
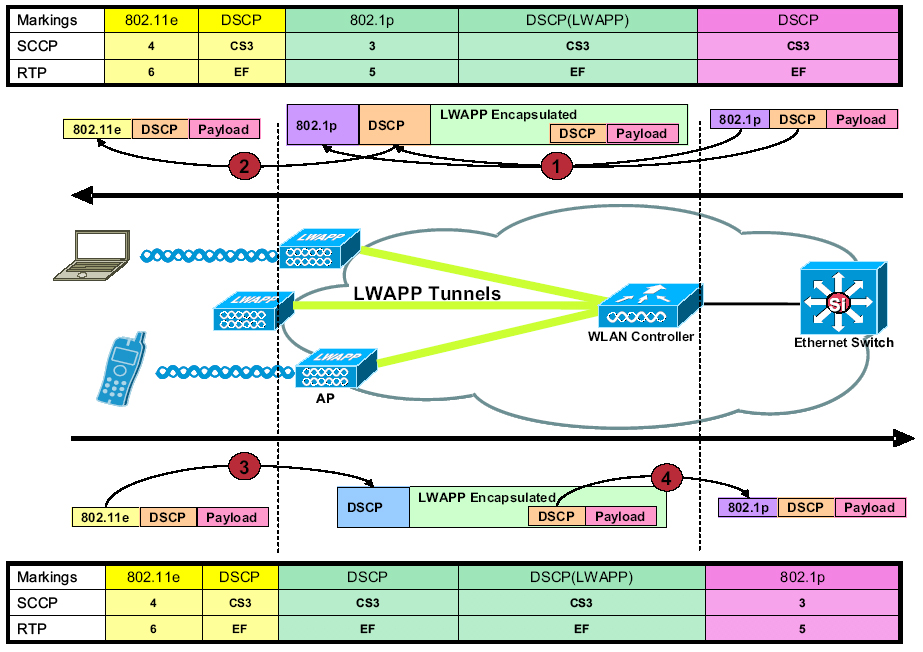
1252 – Requires 802.3at power for dual radio operation and can operate in LWAPP and Autonomous modes.
1242 – Requires 802.3af power to operate and currently in LWAPP mode only. There is a prerequisite of 5.2 firmware or greater on the controller code. Cisco offers 802.11a/g/n and 802.11g/n radio options.
802.11n - Did you know?
- It has real world throughput that clocks in at 160 Mbps or faster—seven times faster than older 802.11g networks.
- At 300 feet, 802.11g performance plummets to 1 Mbps. 802.11n networks operate at up to 70 Mbps—70 times faster than 802.11g.
- The key to this speed is MIMO (multiple input/multiple output) which uses multiple antennas to send and receive digital data in multiple simultaneous radio streams, thus multiplying total performance.
- The approved standard isn’t expected to cause any hardware changes for the larger manufactures.
- 802.11n is backward compatible with legacy device 802.11a,b,g
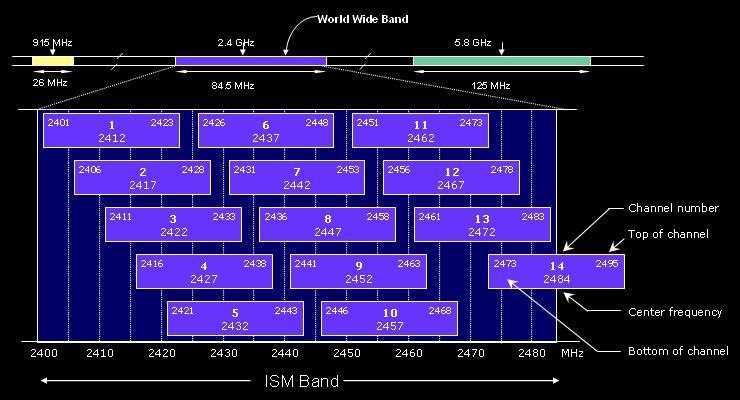
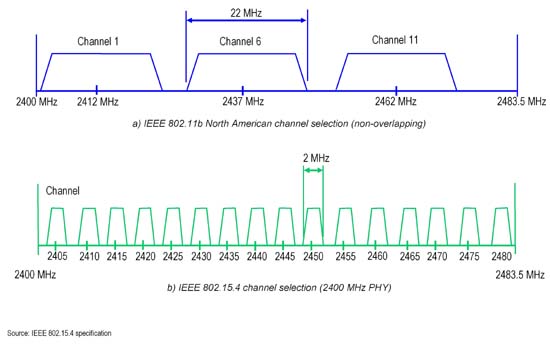
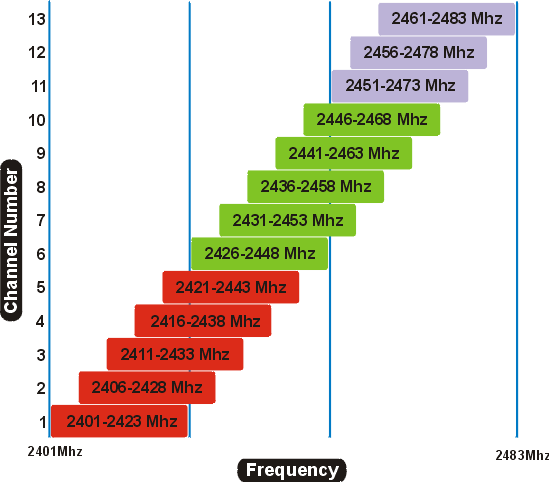
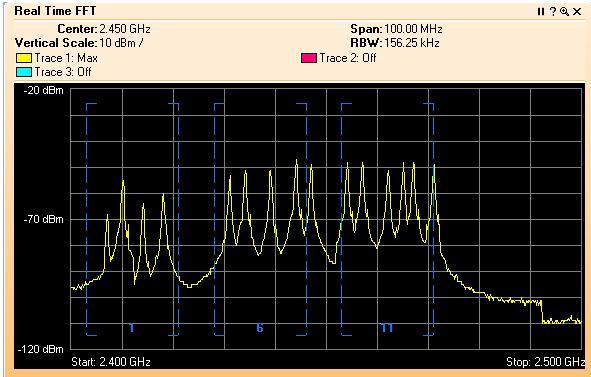
- 802.11n can live in the 5GHz and 2.4 GHz spectrums; ideally 5 GHz to allow for channel bonding
- 802.11n can be deployed with 20 or 40 MHz OFDM channels
- To take full advantage of 802.11n wireless speeds, you need to have gig to the access point!
 George |
George |  Post a Comment |
Post a Comment | 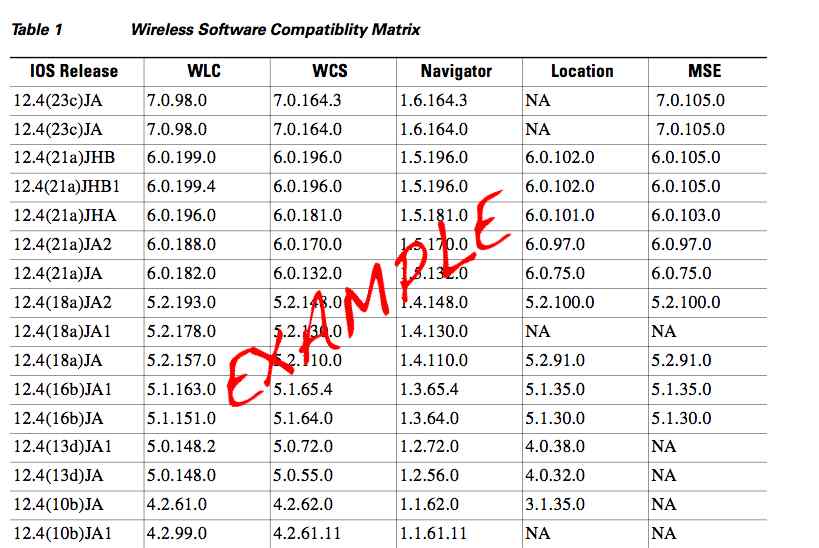




Reader Comments