| 1.0 |
Implementing the Network Infrastructure to Support WLANs
Configuring and Troubleshooting the Network Infrastructure to Support WLANs
|
| 1.01. |
Cisco Discovery Protocol |
| 1.02. |
VTP Modes (Server, Client, Transparent) |
| 1.03. |
VLANs vs. Routed Interfaces |
| 1.04. |
Trunks vs. Access Ports |
| 1.05. |
Load Balancing |
| 1.06. |
Link Aggregation |
| 1.07. |
Spanning Tree Protocol Manipulations |
| 1.08. |
HSRP |
| 1.09. |
Implementing Initial Network Connectivity in WLCs (Management Interface, AP-Manager, Virtual Interface, Service Port Interface, Dynamic Interface Configuration) |
| 1.10. |
VLAN Filtering |
| 1.11. |
WLC as DHCP Server |
| 1.12. |
Wireless Services Module (WiSM) Setup |
| 1.13. |
Configuring Power over Ethernet |
| 1.14. |
Configuring Client Supplicant (ADU, CSSC) to Connect and Authenticate to SSIDs Using EAP, PEAP, EAP-FAST, LEAP and EAP-TLS, WEP, WPA, and WPAv2 |
| 1.15. |
Implementing Relevant Network and Management Services on Switches, APs, LWAPPs, Location Appliance Server, WLCs, and Cisco WCS (NTP, Syslog, DHCP, SNMP, FTP, TFTP, HTTP, HTTPS, Telnet, SSH) |
| 1.16. |
Implementing QoS Services over the Wired Infrastructure |
| 1.17. |
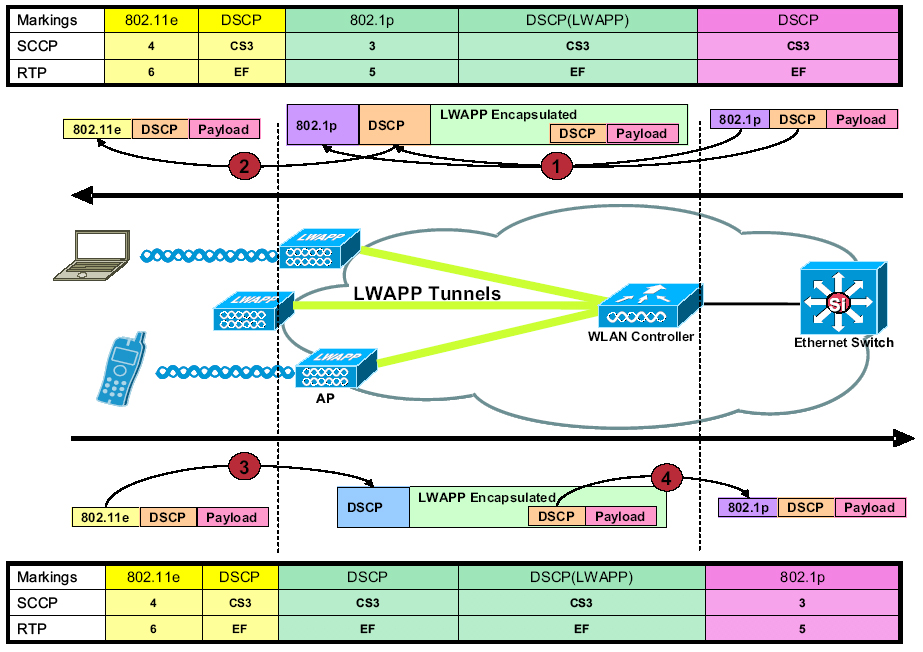
Configuring Marking Using DSCP |
| 1.18. |
Configuring Marking Using IP Precedence |
| 1.19. |
Configuring Marking Using CoS |
| 1.20. |
Configuring CoS to DSCP Mappings |
| 1.21. |
Configuring Policing (Modular QoS) |
| 1.22. |
Static Routing |
| 1.23. |
Basic Dynamic Routing (OSPF, EIGRP) |
| 1.24. |
Subnetting |
| 1.25. |
Troubleshooting Basic Network Connectivity Issues Using Traceroute, Extended Ping, Debugs, etc. |
| 1.26. |
Implementing Basic Enterprise Multicast (IGMP, PIM) |
| 2.0 |
Implementing Autonomous Infrastructure
Configuring and Troubleshooting Autonomous Infrastructure
|
| 2.01. |
Implementing VLAN Trunking |
| 2.02. |
Understanding Mode of Operation for WDS and Infrastructure APs |
| 2.03. |
Implementing a WDS Solution |
| 2.04. |
Implementing a WDS Solution Using a RADIUS Server |
| 2.05. |
Implementing WDS Server Groups |
| 2.06. |
Configuring Infrastructure APs to Use the WDS Service |
| 2.07. |
Understanding the EAP Protocols That Are Supported from a Cisco IOS AP Configured as a Local Authenticator |
| 2.08. |
Configuring NAS Devices to Use the Local Authenticator AP |
| 2.09. |
MAC Authentication vs. EAP Authentication |
| 2.10. |
Assigning Shared Settings from a Group of Users, Such as SSID, VLAN, etc. |
| 2.11. |
Troubleshooting Failing Authentications |
| 2.12. |
Configuring SSID and MBSSID on the Autonomous AP |
| 2.13. |
Configuring and Assigning Different Characteristics to an SSID |
| 2.13.1. |
Security |
| 2.13.2. |
Authentication |
| 2.13.3. |
Encryption |
| 2.14. |
Mapping VLANs to SSIDs |
| 2.15. |
Advanced Radio Setting Parameters (Such as DTIM) |
| 2.16. |
Advertising (or Hiding) SSID Presence to WLAN Clients |
| 2.17. |
Understanding Radio Roles and Their Individual Attributes |
| 2.18. |
AP External Antenna Settings |
| 2.19. |
Impact of the Antenna Characteristics Settings |
| 2.20. |
Configuring Filters on AP Radio Interfaces |
| 2.21. |
AP Access Management |
| 2.22. |
Management Frame Protection |
| 2.23. |
Implementing Multicast Settings (IGMP, PIM) |
| 2.24. |
Implementing Wireless QoS |
| 2.25. |
Implementing Peer-to-Peer Blocking |
| 2.26. |
Configuring Client Access Limitations |
| 2.27. |
Troubleshooting Bridge Connectivity Problems |
| 2.28. |
Bridging Multiple VLANs Across a Point-to-Point Link |
| 2.29. |
Filtering VLANs Across a Point-to-Point Link |
| 2.30. |
Determining and Troubleshooting the Parent-Child Relationship in an 802.11 Bridge Link |
| 2.31. |
Fine-Tuning Point-to-Point Connections to Maintain a Reliable Link |
| 2.32. |
Converting Autonomous APs to LWAPP APs Using Different Methods (Upgrade Tool, Cisco WCS Templates) |
| 3.0 |
Implementing a Unified Infrastructure
Configuring and Troubleshooting a Unified Infrastructure
|
| 3.01. |
WLC Interface Settings (Management Interface, AP-Manager Interface, Virtual Interface, Service Port Interface, Dynamic Interface) |
| 3.02. |
WLC – Tagged vs. Untagged Interfaces |
| 3.03. |
WLC – Link Aggregation (LAG vs. Backup Interface) |
| 3.04. |
WLC – SNMP |
| 3.05. |
Mobility – Asymmetric vs. Symmetric Tunneling |
| 3.06. |
Mobility Anchor |
| 3.07. |
Mobility – Layer 2 and Layer 3 Roaming |
| 3.08. |
Mobility – AP Failover Within a Mobility Group |
| 3.09. |
Mobility – AP Failover Outside a Mobility Group |
| 3.10. |
Troubleshooting Roaming Issues |
| 3.11. |
Implementing WLANs |
| 3.12. |
WLAN to Interface Mapping |
| 3.13. |
WLANs – Configuring DHCP (on Cisco IOS Software, Windows Server, and WLCs) |
| 3.14. |
WLANs – Configuring Peer-to-Peer Blocking |
| 3.15. |
WLANs – Configuring Layer 2 Security |
| 3.15.1. |
802.1X |
| 3.15.2. |
WPA vs. WPA2 |
| 3.15.3. |
Static WEP |
| 3.15.4. |
Cisco Key Integrity Protocol |
| 3.15.5. |
TKIP |
| 3.15.6. |
Cisco Centralized Key Management |
| 3.15.7. |
PSK |
| 3.15.8. |
AES |
| 3.16. |
WLANs – Configuring WLAN Override |
| 3.17. |
WLANs – Configuring Access Point Groups |
| 3.18. |
WLANs – Configuring Radio Policies |
| 3.19. |
WLANs – Configuring AP Modes (Local, H-REAP, Monitor, Sniffer, Rogue Detector) |
| 3.20. |
WLANs – Configuring WLAN QoS Settings |
| 3.21. |
WLANs – Cisco Aironet Extensions |
| 3.22. |
WLANs - Client Exclusion |
| 3.23. |
WLANs – Web Authentication |
| 3.24. |
Implementing Ethernet Multicast Support on the WLC |
| 3.25. |
Configuring a Multicast IP Address |
| 3.26. |
Implementing and Controlling Management Access |
| 3.27. |
Different ACL Types |
| 3.28. |
CPU ACL |
| 3.29. |
Configuring Device Access Control |
| 3.30. |
Configuring Local Management Users |
| 3.31. |
Configuring Cisco Secure ACS (TACACS+ and RADIUS) for Authenticating, Authorizing, and Accounting |
| 3.32. |
Management Users |
| 3.33. |
Controller Redundancy |
| 3.34. |
Configuring Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Controllers |
| 3.35. |
Implementing LWAPP Discovery Mechanisms |
| 3.35.1. |
OTAP |
| 3.35.2. |
Cisco IOS DHC |
| 3.35.3. |
DHCP Option 43 |
| 3.35.4. |
Windows DHCP Server 2003 |
| 3.35.5. |
Windows 2003 DNS |
| 3.35.6. |
Troubleshooting the Discovery Process |
| 3.36. |
Implementing Auto-RF to Adapt to Site Requirements |
| 3.37. |
802.11h |
| 3.38. |
Radio Resource Management Settings: |
| 3.38.1. |
Coverage Hole Detection Tuning |
| 3.38.2. |
Dynamic Channel Assignment (DCA) vs. Static |
| 3.38.3. |
Dynamic Transmit Power Control (DTPC) vs. Static |
| 3.38.4. |
RF Groups |
| 3.39. |
Validating Trap Generation, Notifications in Cisco WCS and WLC |
| 3.40. |
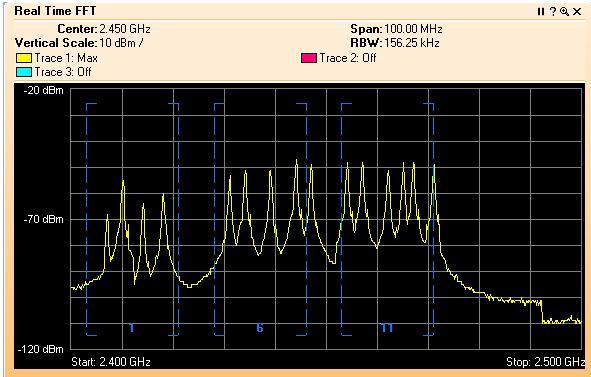
Wireshark and Cisco Spectrum Expert |
| 4.0 |
Implementing Unified Controllers and APs
Configuring and Troubleshooting Unified Controllers and APs
|
| 4.01. |
Implementing Peer-to-Peer Blocking |
| 4.02. |
Implementing Security |
| 4.02.1. |
Configuring WPS Settings |
| 4.02.2. |
Configuring MFP and AP Authentication |
| 4.02.3. |
Configuring AP Authorization |
| 4.02.4. |
Rogue APs |
| 4.02.5. |
Configuring WLC IDS |
| 4.02.6. |
Configuring EAP-FAST |
| 4.02.7. |
Configuring EAP-TLS |
| 4.02.8. |
Configuring PEAP |
| 4.02.9. |
Configuring LEAP |
| 4.03. |
Applying an Access Control List to an Interface |
| 4.04. |
Applying an Access Control List to the Controller CPU |
| 4.05. |
Applying an Access Control List to a WLAN |
| 4.06. |
Implementing Wireless QoS |
| 4.07. |
802.11e Configuration (EDCA, WMM, etc.) |
| 4.08. |
Implementing Local EAP Authentication Against the Local User List |
| 4.09. |
Implementing Local EAP Authentication Against an External LDAP |
| 4.10. |
Implementing Layer 3 Security Policies (Web Authentication, Pass-Through, ACLs) |
| 4.11. |
Creating Guest User Accounts |
| 4.12. |
Lobby Ambassador |
| 4.13. |
Web Authentication |
| 4.14. |
Configuring Wired Guest Access (With or Without Anchor Controller) |
| 4.15. |
Configuring Wireless Guest Access (With or Without Anchor Controller) |
| 4.16. |
Anchor Controller |
| 4.17. |
Implementing Layer 2 Security Policies |
| 4.17.1. |
802.1X |
| 4.17.2. |
WPA vs. WPA2 |
| 4.17.3. |
Static WEP |
| 4.17.4. |
Cisco Key Integrity Protocol |
| 4.17.5. |
TKIP |
| 4.17.6. |
Cisco Centralized Key Management |
| 4.17.7. |
PSK |
| 4.17.8. |
AES |
| 4.17.9. |
Mac Filtering |
| 4.18. |
Implementing Local DHCP Services for Clients on the WLC |
| 4.19. |
Implementing AAA (WLC to RADIUS and LDAP) |
| 4.20. |
Configuring the Cisco Secure ACS (RADIUS, TACACS+) Server |
| 4.20.1. |
ACS – User Setup Parameters |
| 4.20.2. |
ACS – Group Setup Parameters |
| 4.20.3. |
ACS – Network Configuration Parameters |
| 4.20.4. |
ACS – System Configuration Parameters |
| 4.20.5. |
ACS – External User Database Settings |
| 4.20.6. |
ACS – Reports and Activity |
| 4.20.7. |
ACS – Create and Enroll Server Certificate |
| 4.20.8. |
ACS – Global Authentication |
| 4.20.9. |
ACS – Group Mappings |
| 4.20.10. |
ACS – VLAN Assignment |
| 4.21. |
Adding AAA Clients |
| 4.22. |
Troubleshooting Client Connectivity Problems Using Extended Pings, Traceroute, and Debugs |
| 5.0 |
Implementing Cisco Unified WCS and Location
Configuring and Troubleshooting Cisco Unified WCS and Location
|
| 5.01. |
Managing Cisco WCS User Accounts |
| 5.02. |
Adding Controllers to Cisco WCS |
| 5.03. |
Implementing Location Appliance Server to Cisco WCS |
| 5.04. |
SNMP |
| 5.05. |
Creating and Deploying Controller Templates |
| 5.06. |
Preparing Import Building and Floor Map |
| 5.06.1. |
AP Placement |
| 5.06.2. |
Antenna Orientation |
| 5.06.3. |
Calibration |
| 5.07. |
Creating a Floor Coverage Proposal Using the Planning Mode Tool |
| 5.08. |
Performing Maintenance Operations |
| 5.09. |
Performing System Tasks |
| 5.10. |
Tracking Parameters |
| 5.11. |
Filtering Parameters |
| 5.12. |
History Parameters |
| 5.13. |
Notification Parameters |
| 5.14. |
Asset Information |
| 5.15. |
Tune Location Services |
| 5.15.1. |
Tracking Parameters |
| 5.15.2. |
Notifications |
| 5.15.3. |
Timers |
| 5.16. |
Validating Client Connectivity and Troubleshooting the Client via Cisco WCS and WLC |
| 5.17. |
Validating Location Information in Cisco WCS and WLC |
| 5.18. |
Validating Security Events with Cisco WCS and WLC |
| 5.18.1. |
IDS |
| 5.18.2. |
Rogue Detection, Management |
| 5.18.3. |
Alarms and Events |
| 5.18.4. |
Alerts |
| 5.19. |
Validating Trap Generation and Notifications in Cisco WCS and WLC |
| 5.20. |
Running Reports |
| 5.21. |
Troubleshooting Client Roaming |
| 5.22. |
Troubleshooting Client Connectivity Issues |
| 6.0 |
Implementing Voice over Wireless
Configuring and Troubleshooting Voice over Wireless
|
| 6.01. |
Implementing Support for Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7920 and 7921 Deployments for both Unified and Autonomous |
| 6.02. |
Configuring Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7920 and 7921 to Join the Call Manager |
| 6.03. |
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7920 and 7921 Profile Configuration |
| 6.04. |
Implementing Security Settings (Encryption and Authentication) on Phone and Infrastructure |
| 6.04.1. |
802.1X |
| 6.04.2. |
WPA vs. WPA2 |
| 6.04.3. |
Static WEP |
| 6.04.4. |
Cisco Key Integrity Protocol |
| 6.04.5. |
TKIP |
| 6.04.6. |
Cisco Centralized Key Management |
| 6.04.7. |
PSK |
| 6.04.8. |
AES |
| 6.05. |
Fast Secure Roaming |
| 6.06. |
Configuring Voice QoS |
| 6.06.1. |
EDCA |
| 6.06.2. |
WMM |
| 6.06.3. |
CAC |
| 6.06.4. |
802.11e |
| 6.07. |
Configuring End-to-End QoS Marking (over Both Wired and Wireless Infrastructure) |
| 6.08. |
Audit Voice Deployment |
| 6.09. |
Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues |
 Friday, April 9, 2010 at 4:05AM
Friday, April 9, 2010 at 4:05AM 
 autonomous,
autonomous,  web interface
web interface