802.11 Client Active and Passive Scanning
 Monday, January 11, 2010 at 11:45PM
Monday, January 11, 2010 at 11:45PM
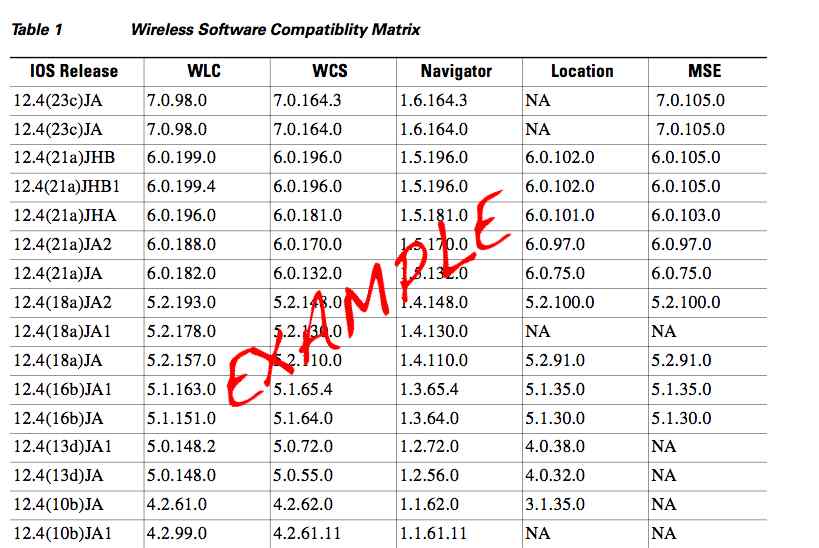
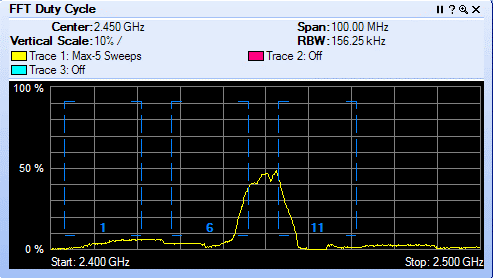
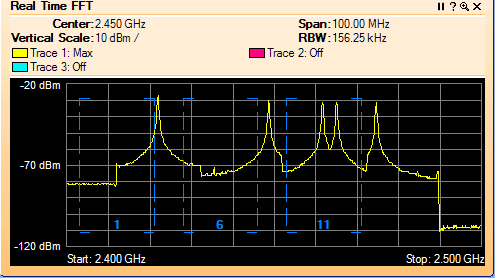
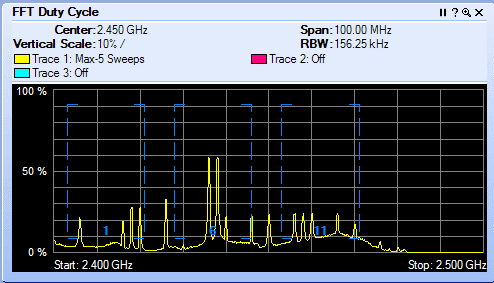
It is important to understand the difference between active and passive client scanning. Here is an overview ~ Wireless clients learn about available APs by scanning other IEEE 802.11 channels for available APs on the same WLAN/SSID. Scanning other IEEE 802.11 channels can be performed actively or passively as follows:
Active scan—Active scanning occurs when the client changes its IEEE 802.11 radio to the channel being scanned, broadcasts a probe request, and then waits to hear any probe responses (or periodic beacons) from APs on that channel (with a matching SSID). The IEEE 802.11 standards do not specify how long the client should wait, but 10 ms is a representative period. The probe request frames used in an active scan are one of two types:

Directed probe—The client sends a probe request with a specific destination SSID; only APs with a matching SSID will reply with a probe response
Broadcast probe—The client sends a broadcast SSID (actually a null SSID) in the probe request; all APs receiving the probe-request will respond, with a probe-response for each SSID they support.
During a channel scan, the client is unable to transmit or receive client data traffic. There are a number of approaches clients take to minimize this impact to client data traffic:
•Background scanning—Clients may scan available channels before they need to roam. This allows them to build-up knowledge of the RF environment and available APs so they may roam faster if it becomes necessary. Impact to client traffic can be minimized by only scanning when the client is not actively transmitting data, or by periodically scanning only a single alternate channel at a time (scanning a single channel incurs minimal data loss)
•On-roam scanning—In contrast with background, on-roam scanning occurs after a roam has been determined necessary. Each vendor/device may implement its own algorithms to minimize the roam latency and the impact to data traffic. For example, some clients might only scan the non-overlapping channels.
Typical Scanning Behavior
Although most client roaming algorithms are proprietary, it is possible to generalize the typical behavior.
Typical wireless client roam behavior consists of the following activities:
•On-roam scanning—This ensures clients have the most up-to-date information at the time of the roam.
•Active scan—An active scan is preferred over a passive scan, due to lower latency when roaming.
There are some informational attributes that may be used to dynamically alter the roam algorithm:
•Client data type—For example, voice call in progress
•Background scan information—Obtained during routine periodic background scans
Ways in which attributes can be used to alter the scan algorithm include: •Scan a subset of channels—For example, information from the background scan can be used to determine which channels are being used by APs in the vicinity. •Terminate the scan early—For example, if a voice call is in progress, the first acceptable AP might be used instead of waiting to discover all APs on all channels. •Change scan timers—For example, if a voice call is in progress, the time spent waiting for probe responses might be shortened during an active scan.
From -- Cisco Voice Over Wireless LAN 4.1 Design Guide