Liquid Antenna - (Sea Water Antenna)
 Saturday, September 4, 2010 at 12:11PM
Saturday, September 4, 2010 at 12:11PM Cisco: 802 11 frames with Cisco VIP George Stefanick
Fluke Networks: Minimize Wi Fi Network Downtime
Aruba: Packets never lie: An in-depth overview of 802.11 frames
ATM15 Ten Talk “Wifi drivers and devices”
Houston Methodist Innovates with Wireless Technology
Bruce Frederick Antennas (1/2)
Bruce Frederick dB,dBi,dBd (2/2)
Cisco AP Group Nugget
Shawn Jackman (Jack) CWNE#54 is a personal friend and has been a mentor to me for many years. I've had the pleasure and opportunity to work with Jack for 4 years. Jack is a great teacher who takes complex 802.11 standards and breaks them down so almost anyone can understand the concept at hand. I'm excited for you brother. Great job and job well done! Put another notch in the belt!
 Saturday, September 4, 2010 at 12:11PM
Saturday, September 4, 2010 at 12:11PM  Wednesday, September 1, 2010 at 10:34PM
Wednesday, September 1, 2010 at 10:34PM http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/ps4555/products_tech_note09186a008074fed9.shtml
Note: These steps optimize roaming delays at the driver layer and are applicable to all authentication types. If 802.1x authentication is used, there might be additional optimizations possible, which are outside the scope of this document.
Note: Optimizing for faster roaming can potentially contribute to increased battery use and to reduced throughput.
Use ADU client software version 4.4 or later.
Set the BSS Aging Interval to 30, and set the Scan Valid Interval to 20.
Complete these steps in order to set these two parameters via the Windows control panel:
Go to Windows Explorer.
Right-click My Network Places.
Choose Properties from the drop-down list.
Right-click Wireless Network Connection#, where # is the instance number of the Cisco CB21AG Wireless LAN adapter.
Choose Properties from the drop-down list. The Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog box appears.
Click Configure.
Click the Advanced tab.
Set the BSS Aging Interval to 30, and set the Scan Valid Interval to 20.
These parameter values are the absolute lowest permitted values and should not be set any lower. The default values are 120 for BSS Aging Interval and 60 for Scan Valid Interval.
If your access point coverage permits it, configure the client profile in the ADU only to use the 5 GHz (802.11a) or 2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) band, not both. In order to configure the client profile, complete these steps:
Launch the ADU client software.
Click the Profile Management tab, highlight the profile of interest, and click Modify.
Click the Advanced tab.
Under Wireless Mode, uncheck the rates that you do not intend to use.
If you do not use the ADU to manage the CB21AG, you must use registry settings in order to select the rates. Complete these steps:
Choose Start > Run, and type regedit in order to launch the Registry Editor.
Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > System > CurrentControlSet > Control > Class > {4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002bE10318}.
Right-click the 4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002bE10318 folder, and choose Find.
Type NetBand in the search field in order to locate the NetBand variable. This is under an [instance] four-digit subkey that has a DriverDesc value of Cisco Aironet 802.11a/b/g Wireless Adapter.
The NetBand REG_SZ variable is a bitmask of supported rates. By default this is 15. The values are:
802.11a 0x01 (not used) 0x02 802.11b 0x04 802.11g 0x08 (not used) 0x10
For example, in order to support only 11b and 11g rates, this is 0x04 + 0x08 = 0x0C = 12 decimal.
 Monday, August 30, 2010 at 8:55PM
Monday, August 30, 2010 at 8:55PM I use my iPad mainly for reading , some tunes and the cool apps. Recently, I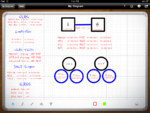 <<<< CLICK ME >>>> wanted to find a
<<<< CLICK ME >>>> wanted to find a
good whiteboard app. So I surfed and found most were just “finger drawing”. I also had a need for a VGA output and one that can be easy to use and looked semi professional (for a whiteboard drawing). In my search I came across Whiteboard HD.
Whiteboard HD allows you VGA output, ease of e-mailing and is great for collaboration. As a network engineer we like to draw with network ICONS. Well they don’t have “network” ICONS, YET. But you can use other shapes and label for identification. I did email support and they said network ICONs are on the way.
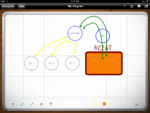 <<<< CLICK ME >>>>The app took a little while to get use to. But after a week I am breezing through the screens. With any new technology you need to embrace and have an open mind. Whiteboard HD isn’t that bad and the best I’ve found so far for my needs. Its like under $8
<<<< CLICK ME >>>>The app took a little while to get use to. But after a week I am breezing through the screens. With any new technology you need to embrace and have an open mind. Whiteboard HD isn’t that bad and the best I’ve found so far for my needs. Its like under $8
Here are a few examples …
If you used a better Whiteboard app please do share !
 Sunday, August 29, 2010 at 11:28AM
Sunday, August 29, 2010 at 11:28AM

http://www.my80211.com/home/2010/5/15/take-a-peek-inside-ciscos-wireless-gear-literally.html
 Saturday, August 21, 2010 at 11:10AM
Saturday, August 21, 2010 at 11:10AM  (Wi-Fi Aerial Surveillance Platform). It's an autonomous Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) that we built in our garage with onboard war-driving gear, among other things.
(Wi-Fi Aerial Surveillance Platform). It's an autonomous Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) that we built in our garage with onboard war-driving gear, among other things.  Tuesday, August 17, 2010 at 7:56AM
Tuesday, August 17, 2010 at 7:56AM You will need Microsoft Visio Standard or Professional in order to see these stencils correctly. Be sure to download the add-ons to enjoy the full functionality of all the Cisco Visio Stencils listed below.
The documents listed for download on this page are .vss files within .zip files
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/prod_cat_visios.html
 Monday, August 16, 2010 at 6:51AM
Monday, August 16, 2010 at 6:51AM Note: Cisco WCS software release 7.0 is not affected by this vulnerability. Cisco WCS version 7.0.164.0 (which is the first 7.0 version) already contains the fix for this vulnerability. Cisco WCS software releases prior to 6.0 are not affected by this vulnerability.
(which is the first 7.0 version) already contains the fix for this vulnerability. Cisco WCS software releases prior to 6.0 are not affected by this vulnerability.
The version of WCS software installed on a particular device can be found via the Cisco WCS HTTP management interface. Choose Help > About the Software to obtain the software version.
Cisco WCS enables an administrator to configure and monitor one or more WLCs and associated access points.
A SQL injection vulnerability exists in Cisco WCS. Exploitation could allow an authenticated attacker to modify system configuration; create, modify and delete users; or modify the configuration of wireless devices managed by WCS.
This vulnerability is documented in Cisco bug ID CSCtf37019 ( registered customers only) and has been assigned Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) ID CVE-2010-2826.
Read more about this field notice:
 Sunday, August 8, 2010 at 1:38PM
Sunday, August 8, 2010 at 1:38PM The Vocera Advisory states:
Vocera is aware of an issue that customers are experiencing after moving to Cisco WLC version 6.0.199 that manifests itself in a substantial increase in difficulty with badge communications to the Vocera Application Server over the network. Badges will display "Searching For Server" or "Searching For AP."
Vocera is working closely with Cisco and its mutual customers on the problem.
Please consult with Vocera Technical Support and Cisco TAC before upgrading to 6.0.199.
 Friday, July 23, 2010 at 6:56PM
Friday, July 23, 2010 at 6:56PM Look at the resolved caveats. There are some BIG problems resolved with this reelase.
Note:6.0 is a MD train and 6.0.199.0 is a potential MD / AW release. 6.0.199.0 release will be marked with MD / AW Tag after few weeks of customer adaptation and completion of AW release certification
 Monday, July 5, 2010 at 9:53PM
Monday, July 5, 2010 at 9:53PM TSN stands for (Transition Security Network). TSN supports both RSN and pre-RSN legacy authentication and encryption on the same BSS.
Example – Think of WEP with WPA and/or WPA2 enabled on the same BSS. Pre-RSN + RSN = TSN
Suppose your WLAN was secured with WEP and you wanted to upgrade to WPA2 . Instead of having to manage another WLAN and add additional wireless utilization (each WLAN you add you increase wireless utilization) you can modify the current WLAN to allow for WPA2 security.
Cisco often references TSN as a “migration” WLAN. I was emailed today about adding a config for a Cisco autonomous ap with TSN.
Our SSID is: wep-wpa2
RSNIE: You will notice the below capture the Group Cipher is Wep104 (WEP128). This is our indication WEP is enabled on this BSS. Since all stations share a single group encryption the lowest common denominator is used. In this case it is Wep104 (WEP128).
Some other areas of interest, the Pairwise Cipher code 00-0F-AC 4. This is our other indication AES-CCMP is being used.
NOTE:
OUI Suite Type Definition
00-0F-AC 0 Use the group cipher suite (only valid for pairwise ciphers)
00-0F-AC 1 WEP-40
00-0F-AC 2 TKIP
00-0F-AC 3 Reserved
00-0F-AC 4 CCMP
Since we are in the frame, let me share what the AUTH KEY MANAGEMENT means. This is were the RSN authentication type lives. You will see 2 types, 00-0F-AC1 for 802.1X or 00-0F-AC2 fo PSK. In our example we are using PSK.
Authentication and key management suites
OUI Suite type Authentication Key management
00-0F-AC 1 802.1X or PMK caching Key derivation from preshared master key
00-0F-AC 2 Pre-shared key Key derivation from pre-shared key

Configuration Notes:
SSID is wep-wpa2
WPA PSK: WPA2/AES
PSK: 1234567890
WEP KEY: Slot 3
WEP KEY: 128 / 12345678901234567890123456
Logon Cisco / Cisco
!
version 12.4
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname ap
!
enable secret 5 $1$/d5u$WOD0P0tI3GSizQKugBNyj0
!
no aaa new-model
no ip domain lookup
!
!
dot11 syslog
!
! dot11: dot11 ssid wep-wpa2 is the SSID that your authentication
! configuration will be applied
!
! Authentication OPEN: Auth OPEN allows open auth for WEP
! Authentication Key-Management: Key-Man WPA V2 optional allows WPA2 with ! the optional command meaning WPA and WEP can be used
! WPA-PSK: This is your key (note its encrypted)
dot11 ssid wep-wpa2
authentication open
authentication key-management wpa version 2 optional
wpa-psk ascii 7 135445415F59527D737D78
!
!
username Cisco password 7 02250D480809
!
bridge irb
!
! Dot11Radio0: This is your 802.11b/g radio where you encryption will live
! Encrypt: Key 3 is the slot, 128 bit is the length, next is your key and !then you are telling the ap that slot 3 is a transmit key
! Encrypt: Mode Cipher aes-ccm and wep128 is telling the radio what
! encryption modes to use. In this case use aes-ccmp AND WEP128
!
interface Dot11Radio0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
!
encryption key 3 size 128bit 7 904856427E9D21265549561E467E transmit-key
encryption mode ciphers aes-ccm wep128
!
ssid wep-wpa2
!
station-role root
bridge-group 1
bridge-group 1 subscriber-loop-control
bridge-group 1 block-unknown-source
no bridge-group 1 source-learning
no bridge-group 1 unicast-flooding
bridge-group 1 spanning-disabled
!
interface Dot11Radio1
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
!
encryption key 3 size 128bit 7 8F156E346C961F07447BA1D43824 transmit-key
encryption mode wep mandatory
dfs band 3 block
channel dfs
station-role root
bridge-group 1
bridge-group 1 subscriber-loop-control
bridge-group 1 block-unknown-source
no bridge-group 1 source-learning
no bridge-group 1 unicast-flooding
bridge-group 1 spanning-disabled
!
interface FastEthernet0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
duplex auto
speed auto
bridge-group 1
no bridge-group 1 source-learning
bridge-group 1 spanning-disabled
!
interface BVI1
ip address 10.10.0.30 255.255.0.0
no ip route-cache
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
ip http help-path http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/779/smbiz/prodconfig/help/eag
bridge 1 route ip
!
!
!
line con 0
line vty 0 4
login local
!
end
 Sunday, July 4, 2010 at 4:34PM
Sunday, July 4, 2010 at 4:34PM RSN stands for (Robust Security Network) which was defined in the 802.11i - 2004 standard. This was later rolled under the 802.11-2007 standard (clause 8). The purpose of RSN is to provide stronger encryption and authentication methods.
RSNA stands for (Robust Security Network Association). RSNA requires (2) 802.11 stations to establish procedures to authenticate and associate with each other as well as create dynamic encryption keys through the 4-way handshake. *Note an access point is also a referenced as a station* The 802.11-2007 standard defines two classes of security methods pre-RSNA and RSNA. RSNA security methods use either TKIP/RC4 or CCMP/AES. This leads me to believe that WPA/TKIP is a RSNA as well. Although not under the RSNIE.
RSNIE stands for (Robust Security Network Information Element). RSNIE is the information element found in certain management frames. The purpose of this information element is to show station compatibilities. RSNIE can identify encryption capabilities and authentication type (802.1X/EAP) and (PSK)
NOTE: There are ONLY 4 types of 802.11 frames that contain the RSN Information Element (RSNIE). Remember (2) of these packets come from the (BSS) access point and (2) of them come from the station. The following FRAMES contain the RSNIE (RSN INFORMATION ELEMENT) when WPA2 / 802.11i is enabled on the BSS.
ACCESS POINT (BSS): BEACON and PROBE RESPONSE frames
CLIENT (Station) : ASSOCIATION RESPONSE and REASSOCIATION RESPONSE frames
Pre-RSN stands for (Pre-Robust Security Network). A pre-RSN uses static or dynamic WEP keys. Anything WEP is considered Pre-RSN.
TSN stands for (Transition Security Network). TSN supports both RSN and pre-RSN legacy authentication and encryption on the same BSS. Example – Think of WEP with WPA and/or WPA2 enabled on the same BSS. Pre-RSN + RSN = TSN
Below is the RSNIE

Note WPA / TKIP is enabled on this BSS. The WPA information element is populated as you can see. Notice you won’t see an RSNIE.

Note WPA / AES is enabled on this BSS. The WPA information element is populated. Notice you won’t see an RSNIE even though AES is enable. This is because RSN is WPA2 only.

WPA2 / TKIP is enabled on this BSS. The RSN information element is populated. Note you don’t see the WPA information element, because WPA is not selected.

Note WPA2 / AES is enabled on this BSS. The RSN information element is populated. Note you don’t see the WPA information element, because WPA is not selected.

This is an example of a single BSS allowing pre-RSN (WEP) and RSN clients. This becomes beneficial when you want to migrate from WEP to a more secure wireless network such as WPA2.

 Friday, July 2, 2010 at 11:04PM
Friday, July 2, 2010 at 11:04PM You can own the entire book for only 3 tokens! Great cost savings... This is a great reference book and I highly recommend it if you are going for certifications or if you are deploying a WLC.
Identifying Wireless Vulnerabilities
Industry Standards and Associations
Regulatory Compliance
Segmenting Traffic
Configuring Administrative Security
Configuring the Cisco Secure ACS for RADIUS
Authenticating Management Users on TACACS+
Configuring the Cisco Secure ACS for TACACS+
Management via Wireless
Configuring Credentials for APs
Managing WLAN Controller and Cisco WCS Alarms
Configuring WCS Logging and Message Notification
Identifying Security Audit Tools
Cisco Spectrum Expert
WCS Security Reports
PCI DSS Compliance Report
Cisco Security MARS
Configuring EAP Authentication
Understanding the Impact of Security on Application and Client Roaming
Configuring Cisco Secure Services Client (SSC)
Troubleshooting Wireless Connectivity
Understanding Guest Access Architecture
Firewall Rules and DHCP
Configuring Foreign and Anchor Controllers
Configuring Guest Access Accounts
Troubleshooting Guest Access
Introducing the Cisco NAC Appliance Server
Configuring the Controller for Cisco NAC Out-of-Band Operations
Configuring Authentication for the WLAN Infrastructure
Configuring Management Frame Protection
Configuring Certificate Services
Implementing Access Control Lists
Implementing Identity-Based Networking
Troubleshooting Secure Wireless Connectivity
Troubleshooting Issues Using External Tools
Mitigating Wireless Vulnerabilities
Understanding the Cisco End-to-End Security Solutions
Integrating Cisco WCS with Wireless IPS
 Friday, July 2, 2010 at 7:28PM
Friday, July 2, 2010 at 7:28PM The carrier busy test will allow you to see what is going on in an environment from 50,000 feet, but that’s about where it ends. It doesn’t have details like a professional analyzer will provide. You could incorporate other commands like frame retries etc to help better interpret “carrier busy”.
that’s about where it ends. It doesn’t have details like a professional analyzer will provide. You could incorporate other commands like frame retries etc to help better interpret “carrier busy”.
Needless to say, it’s a fun command and if you don’t have the proper tools could help you in a pinch. If you do outdoor bridges, you may already use this command to assist on channel assignment.
On a Cisco autonomous access point you can run a command called 'carrier busy'. The AP will shutdown the respected radio interface and will scan all respected channels and report back with a percentage of channel activity. The channel activity collected includes activity from both 802.11 traffic and interference also sometimes called RFI (Radio Frequency Interference).
What this means, if there is 802.11 traffic and suppose there is interference it will compute a (percentage) to this value. Things to note when you run the carrier busy test the radio will do a shut and all associated clients will lose connectivity between 5 - 8 seconds during the test. After the test the radio will no shut itself and return to production allowing clients to associate again.
I have not found any detailed documentation stating exactly how the access point computes these values. If you have any info please do share!
If your access point has both 802.11g <dot11Radio 0> and 802.11a <dot11Radio 1> radios you can run busy test on either the 2.4 GHz or the 5 GHz spectrums.
ap#dot11 <Radio Interface> carrier busy
ap#show dot11 carrier busy
802.11g = dot11Radio 0
802.11a = dot11Radio 1
ap#dot11 dot11Radio 0 carrier busy
wlc-ap#debug dot11 <Radio Interface> carrier busy
802.11g = dot11Radio 0
802.11a = dot11Radio 1
wlc-ap#debug dot11 dot11Radio 0 carrier busy
This example is a neighboring access point on channel 11 only sending management frames
ap#dot11 dot11Radio 0 carrier busy
*Mar 2 09:07:33.173: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to reset
*Mar 2 09:07:34.173: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to down
Frequency Carrier Busy %
--------- --------------
2412 0
2417 3
2422 0
2427 0
2432 0
2437 0
2442 0
2447 4
2452 5
2457 2
2462 5
*Mar 2 09:07:38.695: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
*Mar 2 09:07:39.695: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
I introduced a microwave oven into the mix. You can see there is a significant increase in channel activity from 2447 - 2462.
ap#dot11 dot11Radio 0 carrier busy
*Mar 2 09:05:52.664: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to reset
*Mar 2 09:05:53.664: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to down
Frequency Carrier Busy %
--------- --------------
2412 1
2417 7
2422 5
2427 1
2432 11
2437 13
2442 10
2447 31
2452 36
2457 42
2462 45
*Mar 2 09:05:58.186: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
*Mar 2 09:05:59.186: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
ap#
In this example I introduced 2 laptops and conducted an ISO download for the purpose of creating 802.11 traffic.
ap#dot11 dot11Radio 0 carrier busy
*Mar 2 09:07:33.173: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to reset
*Mar 2 09:07:34.173: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to down
Frequency Carrier Busy %
--------- --------------
2412 0
2417 3
2422 0
2427 0
2432 0
2437 0
2442 3
2447 9
2452 19
2457 21
2462 23
*Mar 2 09:07:38.695: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
*Mar 2 09:07:39.695: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Dot11Radio0, changed state to up
If you don’t have tools and you are in a pinch the carrier busy test may be a tool you might find helpful. Keep in mind, you will need to incorporate other commands to interpret the carrier busy results.
 Wednesday, June 30, 2010 at 11:29PM
Wednesday, June 30, 2010 at 11:29PM You can own the entire book for only 3 tokens! Great cost savings... This is a great reference book and I highly recommend it if you are going for certifications or if you are deploying a WLC.
Tracking Wireless Clients
 Monday, June 28, 2010 at 10:40PM
Monday, June 28, 2010 at 10:40PM You will have to request this code from Cisco TAC as you will not find this on CCO. Cisco TAC stated 6.x release is tagged as software advisory. They are not recommending this code and if you have it installed you should apply the latest Engineer Special release until the 6.x maintenance release is released. The 6.x maintenance release is expected end of July / early August.
If you have 6.x running today Cisco TAC has advised the following path:
1) Down grade to 5.2.193.0 (ED)
2) Upgrade to 7.0.98.0 (ED)
3) Upgrade to 6.0.196.159 (ES)
AS_4200_6_0_196_159 is a build from 6.0.196.0, and it is an engineering special that resolves the following additional caveats:
CSCta13941 - AP rejecting association request with status code 13
CSCtb02136 - AP with AP Groups and HREAP will not broadcast SSID
CSCtb20125 - CCMP errors on key rotation
CSCtc73503 - Radios are showing Tx power level 0
CSCtd28542 - WLC crash on emWeb due to AP config change
CSCtd97011 - Radio core dump: Neighbor Discovery frames stuck
CSCte19262 - Client Deauthenticated – “Unable to locate AP 00:00:00:00:00:00”
CSCte55219 - radio core dump due to large # of uplink frames in inprog queue
CSCte55458 - Web-Auth: Web page takes a long time to display under heavy load
CSCte62815 - 5508 not passing OSPF Multicast traffic
CSCte78472 - Invalid PHY rate returned on ADDTS response
CSCte81420 - Crash in process: "Dot11 driver "
CSCte89891 - AP doesn't transmit beacons
CSCte92365 - Auto Immune - AP side
CSCte93549 - The dot11a radio not able to pass traffic, tx queue getting filled.
CSCte96140 - Ethernet bridging breaks when the Ethernet interface of AP 1242 flapped
CSCtf23682 - 5508 - AP cannot join with Multicast MAC as gateway (checkpoint)
CSCtf34858 - Clients unable to pass broadcast traffic
CSCtf69598 - Memory leak in AP on CCKM Failure
CSCtc57611 - Delay in Music on Hold on 7925 with HREAP AP CSCtg45014 - CT5508 - CAPWAP Control traffic has incorrect DSCP marking.
CSCtg71658 - Ap power level reset to 0 when upgrading from 5.0 to 6.0.196.158
CSCtd43906 - J: RAP not transmitting after coming up; when shut due to radar
The Engineering Special fix supplied herewith is a Temporary Software Module which has undergone limited testing. This temporary software module is provided “AS-IS” without warranty under the terms of the END USER LICENSE FOR THIS PRODUCT. Please use this software at your own risk. The intention for this code fix is for you to use in your production environment until a released version is available.
 Monday, June 28, 2010 at 10:08PM
Monday, June 28, 2010 at 10:08PM Apple released the iPhone 4 this week. There are early reports of antenna issues. Apparently the antenna design is flawed. Depending on how you hold the phone it could attenuate the signal. Steve Job’s responded to emails , “just don’t hold it like that.” Way to go Jobs! This reminds me of the old analogy “A man goes to the doctor and says, Doc when I do this it really hurts. The Doc responds then don’t do that”.
Job’s responded to emails , “just don’t hold it like that.” Way to go Jobs! This reminds me of the old analogy “A man goes to the doctor and says, Doc when I do this it really hurts. The Doc responds then don’t do that”.
Here is a classic example of a client issue. Customers reported issues almost immediately with cell reception with the new iPhone4. So what gives!? … They didn’t change the cell towers over night (access points)! Their phones changed (clients)!
If you read the reports they are using terms you as wireless engineer should be very familiar with, “attenuation, signal degradation, poor reception”. These are general terms we hear or use ourselves. Wireless is a 2-way communication. Often non wireless educated folks assume when there are issues it is the network and by this I mean the wireless access point or wireless infrastructure. They often don’t consider the wireless client.
I can think back to 2003’ish (or there around) when Intel released the Intel 2200b/g clients. This was around the time Cisco purchased Airespace. If you were in WiFi you surly remember this issue.
For those of you who weren’t, here is a quick recap. The Intel 2200 clients were flawed and were flawed for well over 2 months before Intel released a driver fix. The 2200 driver had big issues! When authenticated and in OFDM rates, Intel 2200 clients would not rate shift down to DSSS. As clients moved away from the access point the rate shifting stopped and the client would drop off the wireless. Of course back then customers always looked at the network. “Its got to be the AP”. Especially the early adopters of the new Cisco/Airespace solution. Immediately people pointed blame at Cisco thinking there was an issue with the new controller solution they purchased from Airespace, which wasn’t the case.
Rumor has it Cisco did an assist with Intel with the replacement driver.
WiFi engineers have more tools, training and hands on experience to quickly troubleshoot these issues. In fact, a good wireless engineer can determine if it’s a potential client issue with a quick wireless client capture and debug at the controller or AP. Manufactures of Wireless clients have also improved, especially Intel since they work closely with Cisco. You will find troubleshooting and diagnostics tools on the client side more today then ever before.
You have to remember wireless clients aren’t created equal. They all hear differently (receive sensitivity) and have different transmit power levels and they all have their own operating behavior (when to roam, how they interpret signal strength, etc). Lets face it, some wireless clients are just crap.
If you are new to WiFi. Wireless clients have an equal part in the communication efforts and should be factored in when troubleshooting. In the case of the iPhone4 issue. The didn’t move the cell towers over night. The client changed!
 Saturday, June 26, 2010 at 9:59AM
Saturday, June 26, 2010 at 9:59AM http://www.networkworld.com/news/2010/060210-atheros-wifi-chipset.html?page=1
Chip maker Atheros Wednesday released samples of its powerful new 802.11n Wi-Fi chipset, which tops out with a maximum data rate of 450Mbps for access points and routers, and a signal that's more consistent and resilient.
The 11n standard uses several innovations to boost data rate and throughput, and to maintain those higher levels consistently over longer distances compared to 802.11abg radios.
Like earlier Atheros 11n silicon, the new AR938x and AR9390 chipsets also have three antennas, part of a technology called multiple input multiple output (MIMO). With multiple antennas tuned to the same channel, the radio uses spectrum more efficiently, increasing overall performance. In addition, with multiple antennas on both ends of the send-receive chain, MIMO systems can recombine reflected signals to enhance them (otherwise these multipath reflections typically disrupt the signal).
Another part of the 11n innovation is using what are called multiple spatial streams, or distinct, separately encoded signals within a single spectral channel. Think of it as sending data in parallel: a lot more data in a given time or a given amount of data in much less time. The impact of multiple antennas and spatial streams is also affected by other optional techniques the vendor may implement.
In the past, Atheros and most other Wi-Fi chip vendors have had at best a three-antenna configuration with two spatial streams, for a maximum data rate of 300Mbps. The new chips are Atheros' first to use three spatial streams, one for each antenna pair, boosting the rate to 400Mbps.
Atheros will offer the new 3x3 chipsets at a "similar price range" to the previous generation chipset, says Tony Hsu, senior director of product marketing for Atheros' networking business unit.
A couple of vendors are offering 4x4 MIMO radios. Quantenna Communications has such a product in trials with a dozen carriers, aiming at multi-media applications within a home. It's a development that emphatically makes sense, says Network World blogger Craig Mathias.
The new products also include a range of 802.11n options, including transmit beam forming, which can be thought of as narrowing and focusing the radio signal to increase its range and decrease the impact of interference. Other techniques are Low Density Parity Check for much more efficient error-correction coding, and Maximum Likelihood equalization algorithms to demodulate the received signal with much greater accuracy than other methods.
Adding these techniques to a three-spatial stream chipset results in 50% greater range or up to 66% higher effective bandwidth, depending on the specific operating conditions, according to Atheros.
Apart from the raw increase in data rate and range, these kinds of advances also mean an improved radio environment for video and other streaming media. According to Atheros, its new 11n silicon can slow down the top data rate to reduce packet loss and latency, thus improving the quality of the video transmission. Other algorithms search for unused radio channels for the video stream. Atheros says the chipsets can support three simultaneous high-definition video streams.
The chipsets are available in sample quantities with full production due to ramp up in the third quarter.
 Thursday, June 24, 2010 at 12:26AM
Thursday, June 24, 2010 at 12:26AM Client can't transmit traffic if it reassociates to an AP within 20 sec
|
Symptom: Base Code: 6.0.182.0, 6.0.188.0, 6.0.196.0
Special Build: Following options are available:
1. Move to 7.0.98.0 Release posted on CCO. Please note, 7.0 is a new feature release. 2. Contact TAC to get a 6.0 Special or Beta release with fixes for the bugs below. 3. Wait for the CCO release of 6.0 MR3 (Maintenance Release), which is planned for July/August 2010
The code is designed for 2100 / 4400 / 5500 / WiSM / WLC3750 / WLCM
This Software Advisory Notice is issued against all the above Wireless LAN Controller software versions due to the following bugs:
|
 Wednesday, June 23, 2010 at 10:53PM
Wednesday, June 23, 2010 at 10:53PM 