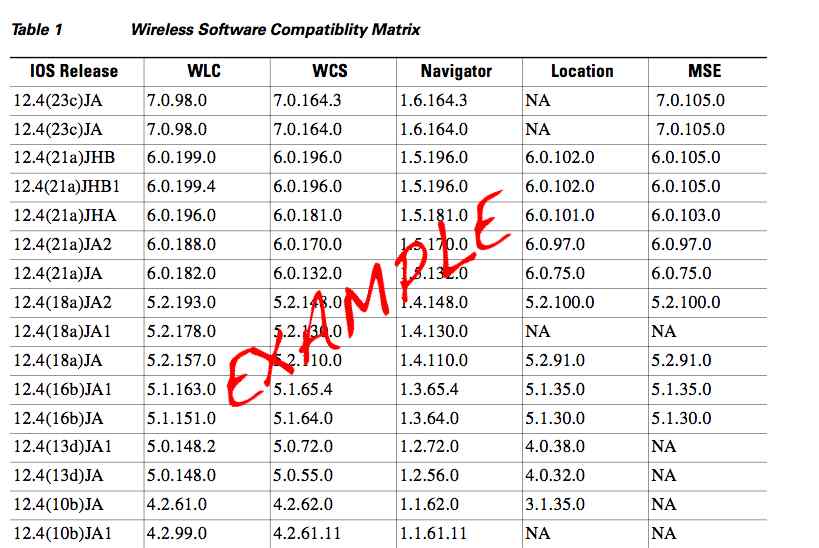
802.11 - Reason Codes and Status Codes
 Sunday, February 7, 2016 at 10:25PM
Sunday, February 7, 2016 at 10:25PM 802.11 - Reason Codes and Status Codes
The 802.11 standard section 8.4 comments on reason codes and status codes. I’ve used these myself when troubleshooting frame captures. These codes provide insight to Wi-Fi related problems like stations connecting and disconnecting. Lets dive in and see what the standard says about reason and status code fields. Then lets look at real world frame captures and see these codes at work.
802.11 Standard Overview
8.4.1.7 Reason Code field
This Reason Code field is used to indicate the reason that an unsolicited notification management frame of type Disassociation, Deauthentication, DELTS, DELBA, DLS Teardown, or Mesh Peering Close was generated. It is contained in the Mesh Channel Switch Parameters element to indicate the reason for the channel switch. It is contained in the PERR element to indicate the reason for the path error. The length of the Reason Code field is 2 octets. The Reason Code field is illustrated in Figure 8-41.
8.4.1.9 Status Code field
The Status Code field is used in a response management frame to indicate the success or failure of a requested operation. The length of the Status Code field is 2 octets. The Status Code field is illustrated in Figure 8-43.
Reason Code Field
When conducting frame captures you can find the reason code in some of the management frames like the response and disassociation frames. I like how the 802.11 standard comments: “unsolicited notification”.
It’s unsolicited information whereby radios can provide connection information.
Example: Disassociation frame with reason code 1. This radio is informing the other radio it’s disassociating for unspecified reasons.

Read this blog post in its entirety here:




Reader Comments