George Stefanick - CWSP Journey, (Chapter 5 – RSN POST#2) - 7/4/2010
 Sunday, July 4, 2010 at 4:40PM
Sunday, July 4, 2010 at 4:40PM George Stefanick - CWSP Journey, (Chapter 5 – RSN POST#2) - 7/4/2010
RSN stands for (Robust Security Network) which was defined in the 802.11i - 2004 standard. This was later rolled under the 802.11-2007 standard (clause 8). The purpose of RSN is to provide stronger encryption and authentication methods.
RSNA stands for (Robust Security Network Association). RSNA requires (2) 802.11 stations to establish procedures to authenticate and associate with each other as well as create dynamic encryption keys through the 4-way handshake. *Note an access point is also a referenced as a station* The 802.11-2007 standard defines two classes of security methods pre-RSNA and RSNA. RSNA security methods use either TKIP/RC4 or CCMP/AES. This leads me to believe that WPA/TKIP is a RSNA as well. Although not under the RSNIE.
RSNIE stands for (Robust Security Network Information Element). RSNIE is the information element found in certain management frames. The purpose of this information element is to show station compatibilities. RSNIE can identify encryption capabilities and authentication type (802.1X/EAP) and (PSK)
NOTE: There are ONLY 4 types of 802.11 frames that contain the RSN Information Element (RSNIE). Remember (2) of these packets come from the (BSS) access point and (2) of them come from the station. The following FRAMES contain the RSNIE (RSN INFORMATION ELEMENT) when WPA2 / 802.11i is enabled on the BSS.
ACCESS POINT (BSS): BEACON and PROBE RESPONSE frames
CLIENT (Station) : ASSOCIATION RESPONSE and REASSOCIATION RESPONSE frames
Pre-RSN stands for (Pre-Robust Security Network). A pre-RSN uses static or dynamic WEP keys. Anything WEP is considered Pre-RSN.
TSN stands for (Transition Security Network). TSN supports both RSN and pre-RSN legacy authentication and encryption on the same BSS. Example – Think of WEP with WPA and/or WPA2 enabled on the same BSS. Pre-RSN + RSN = TSN
Below is the RSNIE

RSNIE is enabled when you choose WPA2 (personal (PSK) or enterprise(802.1X/EAP))
Example #1 WPA/TKIP
Note WPA / TKIP is enabled on this BSS. The WPA information element is populated as you can see. Notice you won’t see an RSNIE. WPA is part of RSN, the sniffer just isnt labling it as such.

Example#2 WPA/AES
Note WPA / AES is enabled on this BSS. The WPA information element is populated. Notice you won’t see an RSNIE even though AES is enable. WPA is part of RSN, the sniffer just isnt labling it as such.

Example#3 WPA2/TKIP
WPA2 / TKIP is enabled on this BSS. The RSN information element is populated. Note you don’t see the WPA information element. Rather you see the RSN element becuase WPA2 was selected.

Example#4 – WPA2/AES
Note WPA2 / AES is enabled on this BSS. The RSN information element is populated. Note you don’t see the WPA information element, because WPA is not selected.

Example#5 TSN (Transition Security Network) WEP , WPA/WPA2 (TKIP/AES)
This is an example of a single BSS allowing pre-RSN (WEP) and RSN clients. This becomes beneficial when you want to migrate from WEP to a more secure wireless network such as WPA2.

 George |
George |  Post a Comment |
Post a Comment | 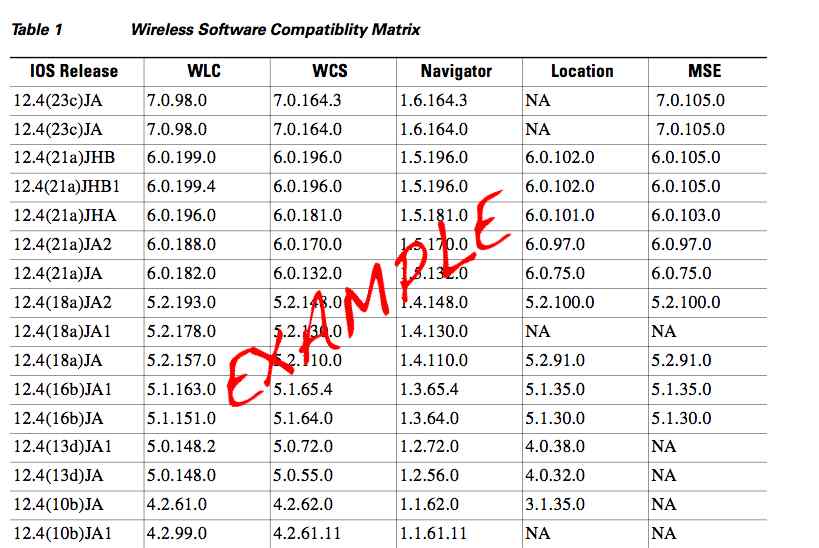




Reader Comments